Gathering detailed insights and metrics for @cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin
Gathering detailed insights and metrics for @cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin
Gathering detailed insights and metrics for @cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin
Gathering detailed insights and metrics for @cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin
Terra Toolkit is a monorepo that contains utility modules for use when developing using Terra components
npm install @cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-pluginTypescript
Module System
Min. Node Version
Node Version
NPM Version
JavaScript (91.84%)
MDX (8.09%)
SCSS (0.05%)
Dockerfile (0.01%)
CSS (0.01%)
Total Downloads
0
Last Day
0
Last Week
0
Last Month
0
Last Year
0
Apache-2.0 License
32 Stars
859 Commits
38 Forks
29 Watchers
76 Branches
66 Contributors
Updated on May 22, 2024
Latest Version
2.6.0
Package Id
@cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin@2.6.0
Unpacked Size
98.66 kB
Size
78.37 kB
File Count
8
NPM Version
lerna/6.6.2/node@v14.21.3+x64 (linux)
Node Version
14.21.3
Published on
Sep 27, 2023
Cumulative downloads
Total Downloads
Last Day
0%
NaN
Compared to previous day
Last Week
0%
NaN
Compared to previous week
Last Month
0%
NaN
Compared to previous month
Last Year
0%
NaN
Compared to previous year
4
1
Webpack plugin that warns when your bundle contains multiple versions of the same package.
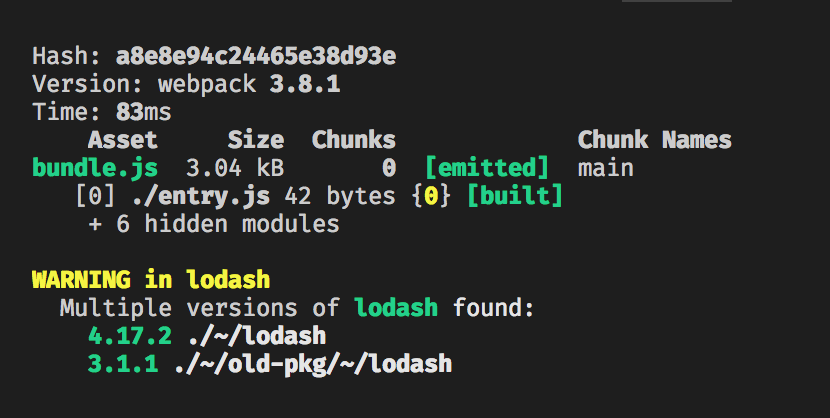
This package is a modified fork of darrenscerri's duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin.
It might be possible that a single package gets included multiple times in a Webpack bundle due to different package versions. This situation may happen without any warning, resulting in extra bloat in your bundle and may lead to hard-to-find bugs.
This plugin will warn you of such cases to minimize bundle size and avoid bugs caused by unintended duplicate packages.
Motivation: https://github.com/webpack/webpack/issues/385 and https://github.com/webpack/webpack/issues/646.
1npm install @cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin --save-dev
Add the plugin to your webpack config:
1var DuplicatePackageCheckerPlugin = require("@cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin"); 2 3module.exports = { 4 plugins: [new DuplicatePackageCheckerPlugin()] 5};
You can also pass an object with configurable options:
1new DuplicatePackageCheckerPlugin({ 2 // Also show module that is requiring each duplicate package (default: false) 3 verbose: true, 4 // Emit errors instead of warnings (default: false) 5 emitError: true, 6 // Show help message if duplicate packages are found (default: true) 7 showHelp: false, 8 // Warn also if major versions differ (default: true) 9 strict: false, 10 /** 11 * Exclude instances of packages from the results. 12 * If all instances of a package are excluded, or all instances except one, 13 * then the package is no longer considered duplicated and won't be emitted as a warning/error. 14 * @param {Object} instance 15 * @param {string} instance.name The name of the package 16 * @param {string} instance.version The version of the package 17 * @param {string} instance.path Absolute path to the package 18 * @param {?string} instance.issuer Absolute path to the module that requested the package 19 * @returns {boolean} true to exclude the instance, false otherwise 20 */ 21 exclude: instance => instance.name === "fbjs", 22 // Emit errors (regardless of emitError value) when the specified packages are duplicated (default: []) 23 alwaysEmitErrorsFor: ['react', 'react-router'], 24});
Strict mode warns when multiple packages with different major versions (such as v1.0.0 vs v2.0.0) exist in the bundle.
Packages with different major versions introduce backward incompatible changes and require either interventions on third-party packages or unsafe workarounds (such as resolving differing package major versions dependencies with a single version).
It is suggested that strict mode is kept enabled since this improves visibility into your bundle and can help in solving and identifying potential issues.
This package was developed and tested using Node 10 up to Node 14. Consumers using Node 16 or greater are advised to use it at their own risk since those versions are not officially supported due to lack of thorough testing.
There are multiple ways you can go about resolving duplicate packages in your bundle, the right solution mostly depends on what tools you're using and on each particular case.
resolve.aliasAdd an entry in resolve.alias which will configure Webpack to route any package references to a single specified path.
For example, if Lodash is duplicated in your bundle, the following configuration would render all Lodash imports to always refer to the Lodash instance found at ./node_modules/lodash.
alias: {
lodash: path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules/lodash'),
}
Note: Aliasing packages with different major versions may break your app. Use only if you're sure that all required versions are compatible, at least in the context of your app
install --flatYarn allows flat installations (yarn install --flat) which will only allow one version of each package to be installed.
If you want more control over your overridden dependency versions and don't feel like using yarn install --flat, yarn supports "selective version resolution" which allows you to enforce specific versions for each dependency.
package.json
{
"dependencies": {
"lodash": "4.17.0",
"old-package-with-old-lodash": "*"
},
"resolutions": {
"old-package-with-old-lodash/lodash": "4.17.0"
}
}
If you use NPM and not Yarn, you can try running npm dedupe. NPM may leave multiple versions of the same package installed even if a single version satisfies each semver of all of its dependants.
If your project is using an old version of a package and a dependency is using a newer version of that package, consider upgrading your project to use the newer version.
If your project has a dependency and it's using an outdated version of a package, file an issue and notify the author to update the dependencies. Let's help keep our projects green and our applications secure, performant and bug-free!

No vulnerabilities found.
Reason
no dangerous workflow patterns detected
Reason
license file detected
Details
Reason
no binaries found in the repo
Reason
Found 27/30 approved changesets -- score normalized to 9
Reason
project is archived
Details
Reason
no effort to earn an OpenSSF best practices badge detected
Reason
security policy file not detected
Details
Reason
detected GitHub workflow tokens with excessive permissions
Details
Reason
project is not fuzzed
Details
Reason
dependency not pinned by hash detected -- score normalized to 0
Details
Reason
SAST tool is not run on all commits -- score normalized to 0
Details
Reason
45 existing vulnerabilities detected
Details
Score
Last Scanned on 2025-07-07
The Open Source Security Foundation is a cross-industry collaboration to improve the security of open source software (OSS). The Scorecard provides security health metrics for open source projects.
Learn More