Gathering detailed insights and metrics for decimal.js
Gathering detailed insights and metrics for decimal.js
Gathering detailed insights and metrics for decimal.js
Gathering detailed insights and metrics for decimal.js
An arbitrary-precision Decimal type for JavaScript
npm install decimal.jsModule System
Min. Node Version
Typescript Support
Node Version
NPM Version
6,506 Stars
166 Commits
475 Forks
74 Watching
3 Branches
19 Contributors
Updated on 28 Nov 2024
JavaScript (99.89%)
HTML (0.11%)
Cumulative downloads
Total Downloads
Last day
-8.7%
3,849,112
Compared to previous day
Last week
2.4%
22,746,005
Compared to previous week
Last month
16%
91,292,422
Compared to previous month
Last year
12.1%
896,780,396
Compared to previous year

No dependencies detected.
An arbitrary-precision Decimal type for JavaScript.
Number.prototype and Math objects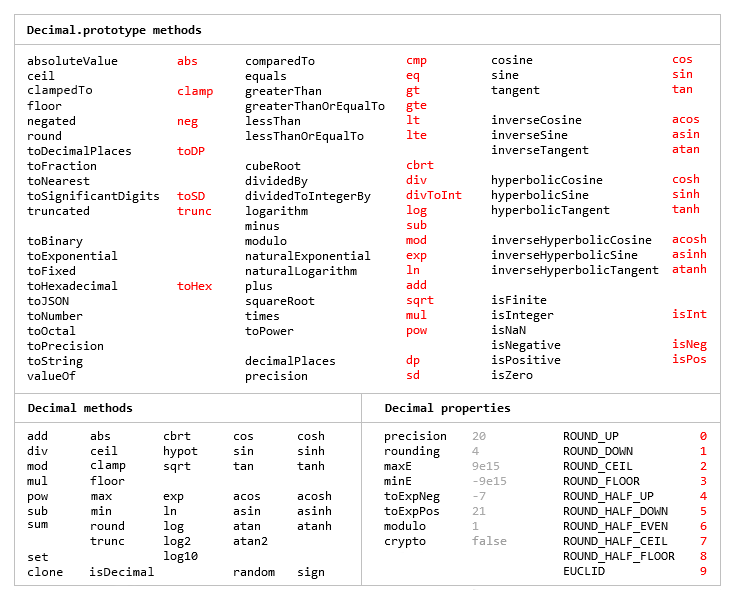
The library is similar to bignumber.js, but here precision is specified in terms of significant digits rather than decimal places, and all calculations are rounded to the precision (similar to Python's decimal module) rather than just those involving division.
This library also adds the trigonometric functions, among others, and supports non-integer powers, which makes it a significantly larger library than bignumber.js and the even smaller big.js.
For a lighter version of this library without the trigonometric functions see decimal.js-light.
The library is the single JavaScript file decimal.js or ES module decimal.mjs.
Browser:
1<script src='path/to/decimal.js'></script> 2 3<script type="module"> 4 import Decimal from './path/to/decimal.mjs'; 5 ... 6</script>
1npm install decimal.js
1const Decimal = require('decimal.js'); 2 3import Decimal from 'decimal.js'; 4 5import {Decimal} from 'decimal.js';
In all examples below, semicolons and toString calls are not shown.
If a commented-out value is in quotes it means toString has been called on the preceding expression.
The library exports a single constructor function, Decimal, which expects a single argument that is a number, string or Decimal instance.
1x = new Decimal(123.4567) 2y = new Decimal('123456.7e-3') 3z = new Decimal(x) 4x.equals(y) && y.equals(z) && x.equals(z) // true
If using values with more than a few digits, it is recommended to pass strings rather than numbers to avoid a potential loss of precision.
1// Precision loss from using numeric literals with more than 15 significant digits. 2new Decimal(1.0000000000000001) // '1' 3new Decimal(88259496234518.57) // '88259496234518.56' 4new Decimal(99999999999999999999) // '100000000000000000000' 5 6// Precision loss from using numeric literals outside the range of Number values. 7new Decimal(2e+308) // 'Infinity' 8new Decimal(1e-324) // '0' 9 10// Precision loss from the unexpected result of arithmetic with Number values. 11new Decimal(0.7 + 0.1) // '0.7999999999999999'
As with JavaScript numbers, strings can contain underscores as separators to improve readability.
1x = new Decimal('2_147_483_647')
String values in binary, hexadecimal or octal notation are also accepted if the appropriate prefix is included.
1x = new Decimal('0xff.f') // '255.9375' 2y = new Decimal('0b10101100') // '172' 3z = x.plus(y) // '427.9375' 4 5z.toBinary() // '0b110101011.1111' 6z.toBinary(13) // '0b1.101010111111p+8' 7 8// Using binary exponential notation to create a Decimal with the value of `Number.MAX_VALUE`. 9x = new Decimal('0b1.1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111p+1023') 10// '1.7976931348623157081e+308'
Decimal instances are immutable in the sense that they are not changed by their methods.
10.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998 2x = new Decimal(0.3) 3x.minus(0.1) // '0.2' 4x // '0.3'
The methods that return a Decimal can be chained.
1x.dividedBy(y).plus(z).times(9).floor() 2x.times('1.23456780123456789e+9').plus(9876.5432321).dividedBy('4444562598.111772').ceil()
Many method names have a shorter alias.
1x.squareRoot().dividedBy(y).toPower(3).equals(x.sqrt().div(y).pow(3)) // true 2x.comparedTo(y.modulo(z).negated() === x.cmp(y.mod(z).neg()) // true
Most of the methods of JavaScript's Number.prototype and Math objects are replicated.
1x = new Decimal(255.5) 2x.toExponential(5) // '2.55500e+2' 3x.toFixed(5) // '255.50000' 4x.toPrecision(5) // '255.50' 5 6Decimal.sqrt('6.98372465832e+9823') // '8.3568682281821340204e+4911' 7Decimal.pow(2, 0.0979843) // '1.0702770511687781839' 8 9// Using `toFixed()` to avoid exponential notation: 10x = new Decimal('0.0000001') 11x.toString() // '1e-7' 12x.toFixed() // '0.0000001'
And there are isNaN and isFinite methods, as NaN and Infinity are valid Decimal values.
1x = new Decimal(NaN) // 'NaN' 2y = new Decimal(Infinity) // 'Infinity' 3x.isNaN() && !y.isNaN() && !x.isFinite() && !y.isFinite() // true
There is also a toFraction method with an optional maximum denominator argument.
1z = new Decimal(355) 2pi = z.dividedBy(113) // '3.1415929204' 3pi.toFraction() // [ '7853982301', '2500000000' ] 4pi.toFraction(1000) // [ '355', '113' ]
All calculations are rounded according to the number of significant digits and rounding mode specified
by the precision and rounding properties of the Decimal constructor.
For advanced usage, multiple Decimal constructors can be created, each with their own independent configuration which applies to all Decimal numbers created from it.
1// Set the precision and rounding of the default Decimal constructor 2Decimal.set({ precision: 5, rounding: 4 }) 3 4// Create another Decimal constructor, optionally passing in a configuration object 5Dec = Decimal.clone({ precision: 9, rounding: 1 }) 6 7x = new Decimal(5) 8y = new Dec(5) 9 10x.div(3) // '1.6667' 11y.div(3) // '1.66666666'
The value of a Decimal is stored in a floating point format in terms of its digits, exponent and sign, but these properties should be considered read-only.
1x = new Decimal(-12345.67); 2x.d // [ 12345, 6700000 ] digits (base 10000000) 3x.e // 4 exponent (base 10) 4x.s // -1 sign
For further information see the API reference in the doc directory.
To run the tests using Node.js from the root directory:
1npm test
Each separate test module can also be executed individually, for example:
1node test/modules/toFraction
To run the tests in a browser, open test/test.html.
Two minification examples:
Using uglify-js to minify the decimal.js file:
1npm install uglify-js -g 2uglifyjs decimal.js --source-map url=decimal.min.js.map -c -m -o decimal.min.js
Using terser to minify the ES module version, decimal.mjs:
1npm install terser -g 2terser decimal.mjs --source-map url=decimal.min.mjs.map -c -m --toplevel -o decimal.min.mjs
1import Decimal from './decimal.min.mjs';

No vulnerabilities found.
Reason
no binaries found in the repo
Reason
license file detected
Details
Reason
0 existing vulnerabilities detected
Reason
Found 6/24 approved changesets -- score normalized to 2
Reason
0 commit(s) and 1 issue activity found in the last 90 days -- score normalized to 0
Reason
no effort to earn an OpenSSF best practices badge detected
Reason
security policy file not detected
Details
Reason
branch protection not enabled on development/release branches
Details
Reason
project is not fuzzed
Details
Reason
SAST tool is not run on all commits -- score normalized to 0
Details
Score
Last Scanned on 2024-11-25
The Open Source Security Foundation is a cross-industry collaboration to improve the security of open source software (OSS). The Scorecard provides security health metrics for open source projects.
Learn More